|
Computer
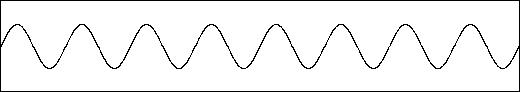
Music: Musc 216 ALIASING is a type of digital noise that results when a sample rate is too low to acurately represent the waveform. Standard practice is to use a sample rate that is greater than TWICE the frequency of the wave. For example, consider the following SINE wave at 8 Hz (8 cycles in ONE second) sampled at 44,100 samples:
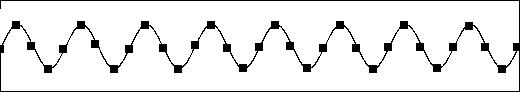
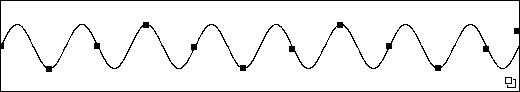
Sampled at 12Hz would resulet in this:
|