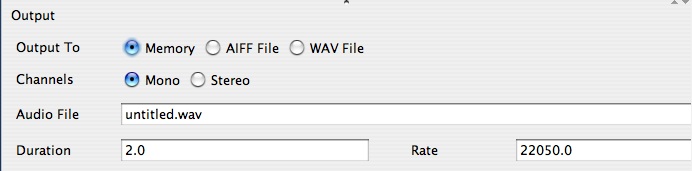
| Computer Music: Musc 216 The sample rate of the patch is determined by a parameter in the Output operator. The only reason you would need to change the sample rate would be if you are using a frequency which is greater than half of the sample. See Nyquist Limit. For example, if the sample rate is set to 22050 samples per second (Hz) and you were using a frequency greater than 11025 Hz, then you would need to set the sample rate higher, sat to 44100 Hz. Otherwise you would create a kind of digital noise known as ALIASING. To set the SAMPLE RATE of your patch: Open the patch you created in Tutorial2.
It is not necessary to change the sample rate of your patch unless you are using a frequency that is greater than half the sample rate. See Nyquist Limit. Otherwise you create more data than is necessary to represent your sound. For example, at a sample rate of 22050 Hz, one minute of monophonic sound equates to approx 2.5 megabytes of memory or disk space. At 44100 Hz, one minute of monophonic sound equals 5 megabytes. A stereo sound would double the amount of memory or disk space. Back to the JSYD Tutorials Index |